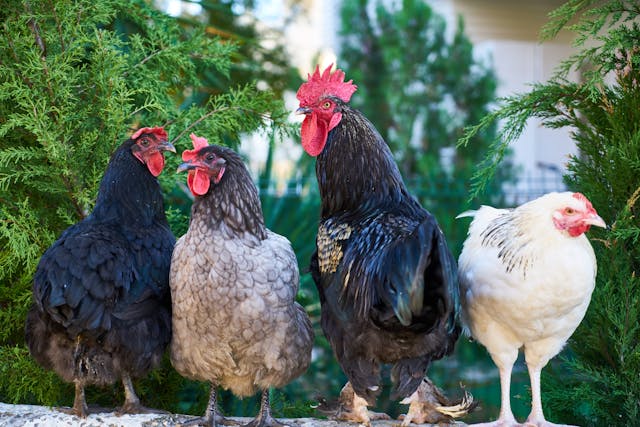
Introduction To Poultry Farming
Poultry farming is the pillar of agriculture. It has been clinically proven that man requires a balanced diet to survive. One of the essential requirements for this balanced diet is protein, which is supplied by meat. Apart from red meat – beef etc., The other class of meat is that of birds. Within this family of birds, You have broilers, layers, ducks, Quails, and turkeys. This not only provides meat, but eggs as well. It is because of their nutritional and economic Importance that many farmers go into their production. Experience has also taught that they are very easy and cheap to maintain hence small-scale farmers can also keep them. Families to provide eggs for their tables can even keep them.
Our task in this section is to look at the different kinds of birds that are kept in the poultry. This includes broilers, layers, turkeys, ducks, and quails. We shall look at their brooding, feeding healthcare, and reproduction techniques.
General features of poultry:
Common words and expressions in poultry rearing
| Concepts | Definition |
| Poultry | All the domesticated birds, raised for meat and eggs |
| Specie | Group of animals characterized by one or many characteristics that make them different from other species. The members of one species are capable of reproduction when they mate with those of the same species |
| Breed | Group of birds with fixed physiological characteristics (Rusticity, Fast growth, egg production) And common morphologic characters (Feather color, legs, color…) |
| Reproduction | The function which enables a group of birds of the same species to multiply themselves by producing other individuals that are similar to them |
| Ratio | Member of females, per male for appropriate reproduction |
| Ration | Required quantity of feed per day per individual for proper reproduction and production of meat and eggs |
| Therapeutic plan | All hygienic, biological, and chemical measures taken by the farmer to avoid an apparition or spreading of diseases in the livestock |
| Disinfection | Operations aiming to avoid contamination of coming flocks of birds by pathogenic agents |
| Sanitary quarantine | Keeping already disinfected poultry house without any beds for a few days to break the development cycle of the pathogenic agents |
| Virus | Micro-organisms that are very minuscule and could never be observed without an electronic microscope |
| Bacteria | Micro-organisms that can be observed with an ordinary microscope |
| Parasite | Living beings whose body comprises many cells and that live on other organisms |
| Antibiotic | Chemical or natural substances, that possess insignificant dosages, can inhibit the growth or destroy bacteria |
| Vitamin | Substances that can be synthesized by organisms. Those substances in minor quantities are required for body maintenance and for essential physiological functions. |
| Index of feed conversion efficiency | This means, the quantity of feed consumed per bird per day (Daily consumed feed) For a given period in grams, Divided by the last weight minus the initial weight in grams |
| Average daily body weight gain | This is the end weight minus the initial weight divided by the period in question in days |
| Density | Number of bed, surface units, (m2) to ensure the vital functions of production and reproduction |
| Laying rate | This is the number of eggs collected for a given period divided by the number of females for the same period in question. This result is multiplied by 100. |
| Mortality rate | Number of dead birds divided by the initial number of birds. The result is multiplied by 100. |
| Fertility rate | Number of fertile eggs divided by the number of hatched eggs. The result is multiplied by 100. |
| Hatching rate | Number of the eggs divided by the number of hatched eggs the result is multiplied by 100 |
What type of poultry to raise?
Poultry rearing in the tropics is justified by economic, social, and environmental motivations. It depends widely on the passion of the farmer for agriculture and the likes of the consumers.
Economic importance of poultry, rearing
The poultry business leads to numerous economic advantages:
- Diversification of incomes
- Valorization of by-products and wastes from food processing industries (Cakes, bran, etc)
- Fast-track activity if the business is well-planned and managed
- Poultry does not require heavy investments at the beginning
- Poultry-rearing techniques are uncomplicated and can be mastered rapidly
Nutritional importance of poultry rearing
- Poultry meat is rich in protein and constitutes one of the most consumed meats in the world
- Because of its high protein content, it plays a fundamental role in the growth of children and good body keeping for adults
- Poultry meat is easily digestible by the human body. It is not subject to many taboos.
Social importance of poultry rearing
- Poetry rearing is an important income-generation activity
- In traditional societies, poultry meat is commonly used for many ceremonies (Weddings, New Year, Christmas, and other celebrations…)
Importance of poultry in the integrated farming system
- The poultry waste is used as organic manure through compost and as a substrate for maggot production
- The feather and the blood constitute interesting ingredients for feed supplements and feed formulation
- The Viscera are used for maggot production, or directly for fish feeding.
Critical assumptions in poultry rearing
- Availability of clean water supply
- The free-range poultry could expose the beds to predators or unsuitable climatic conditions
- Necessity of keeping the surrounding areas clean
- Availability of raw materials for feeds
- Industrial poultry farms require well-skilled personnel and opened market